THE AMERICAN WOODCOCK.
SN’T this American Woodcock, or indeed any member of the family, a comical bird? His head is almost square, and what a remarkable eye he has! It is a seeing eye, too, for he does not require light to enable him to detect the food he seeks in the bogs. He has many names to characterize him, such as Bog-sucker, Mud Snipe, Blind Snipe. His greatest enemies are the pot hunters, who nevertheless have nothing but praise to bestow upon him, his flesh is so exquisitely palatable. Even those who deplore and deprecate the destruction of birds are not unappreciative of his good qualities in this respect.
The Woodcock inhabits eastern North America, the north British provinces, the Dakotas, Nebraska and Kansas, and breeds throughout the range.
Night is the time when the Woodcock enjoys life. He never flies voluntarily by day, but remains secluded in close and sheltered thickets till twilight, when he seeks his favorite feeding places. His sight is imperfect by day, but at night he readily secures his food, assisted doubtless by an extraordinary sense of smell. His remarkably large and handsome eye is too sensitive for the glare of the sun, and during the greater part of the day he remains closely concealed in marshy thickets or in rank grass. In the morning and evening twilight and on moonlight nights, he seeks his food in open places. The early riser may find him with ease, but the first glow from the rays of the morning sun will cause his disappearance from the landscape.
He must be looked for in swamps, and in meadows with soft bottoms. During very wet seasons he seeks higher land—usually cornfields—and searches for food in the mellow plowed ground, where his presence is indicated by holes made by his bill. In seasons of excessive drought the Woodcock resorts in large numbers to tide water creeks and the banks of fresh water rivers. So averse is he to an excess of water, that after continued or very heavy rains he has been known suddenly to disappear from widely extended tracts of country.
A curious habit of the Woodcock, and one that is comparatively little known, is that of carrying its young in order to remove them from danger. So many trustworthy naturalists maintain this to be true that it must be accepted as characteristic of this interesting bird. She takes her young from place to place in her toe grasps as scarcity of food or safety may require.
As in the case of many birds whose colors adapt them to certain localities or conditions of existence, the patterns of the beautiful chestnut parts of the Woodcock mimic well the dead leaves and serve to protect the female and her young. The whistle made by their wings when flying is a manifestation of one of the intelligences of nature.
The male Woodcock, it is believed, when he gets his “intended” off entirely to himself, exhibits in peculiar dances and jigs that he is hers and hers only, or rises high on the wing cutting the most peculiar capers and gyrations in the air, protesting to her in the grass beneath the most earnest devotion, or advertising to her his whereabouts.
THE WOODCOCK.
Here is a bird that is not often seen in the daytime. During the day he stays in the deep woods or among the tall marsh grasses.
It is at twilight that you may see him. He then comes out in search of food.
Isn’t he an odd-looking bird? His bill is made long so that he can bore into the soft ground for earthworms.
You notice his color is much like the Ruffed Grouse in June “BIRDS.” This seems to be the color of a great many birds whose home is among the grasses and dried leaves. Maybe you can see a reason for this.
Those who have watched the Woodcock carefully, say that he can move the tip end of the upper part of his bill. This acts like a finger in helping him to draw his food from the ground.
What a sight it must be to see a number of these weird-looking birds at work getting their food. If they happen to be in a swampy place, they often find earthworms by simply turning over the dead leaves.
If there should be, near by, a field that has been newly plowed, they will gather in numbers, at twilight, and search for worms.
The Woodcock has short wings for his size. He seems to be able to fly very fast. You can imagine how he looks while flying—his long bill out in front and his legs hanging down.
Summary
AMERICAN WOODCOCK.—Philohela minor. Other names: “Bog-sucker,” “Mud Snipe,” “Blind Snipe.”
Range—Eastern North America, breeding throughout its range.
Nest—Of dried leaves, on the ground.
Eggs—Four; buffy, spotted with shades of rufous.
***************
Lee’s Addition:
You will seek me and find me, when you seek me with all your heart. (Jeremiah 29:13 ESV)
For the gate is narrow and the way is hard that leads to life, and those who find it are few. (Matthew 7:14 ESV)
That they should seek the Lord, if haply they might feel after him, and find him, though he be not far from every one of us: (Acts 17:27 KJV)
Thinking about how the Woodcock is protected by the way the Lord created it to blend in to the leaves and bark reminded me of trying to find something. The above verses came to mind. I trust we are all seeking the Lord, His Salvation and His Blessings.
The American Woodcock (Scolopax minor), sometimes colloquially referred to as the Timberdoodle, is a small chunky shorebird species found primarily in the eastern half of North America. Woodcock spend most of their time on the ground in brushy, young-forest habitats, where the birds’ brown, black, and gray plumage provides excellent camouflage.
Because of the male Woodcock’s unique, beautiful courtship flights, the bird is welcomed as a harbinger of spring in northern areas. It is also a popular game bird, with about 540,000 killed annually by some 133,000 hunters in the U.S.
The American Woodcock is the only species of Woodcock inhabiting North America. Although classified with the sandpipers and shorebirds in Family Scolopacidae, the American Woodcock lives mainly in upland settings. Its many folk names include timberdoodle, bogsucker, night partridge, brush snipe, hokumpoke, and becasse.
The American Woodcock has a plump body, short legs, a large, rounded head, and a long, straight bill. Adults are 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm) long and weigh 5 to 8 ounces (140 to 230 g). Females are considerably larger than males. The bill is 2.5 to 2.75 inches (6.3 to 7.0 cm) long.
“Woodcock, with attenuate primaries, nat. size.” 1891.
The plumage is a cryptic mix of different shades of browns, grays, and black. The chest and sides vary from yellowish white to rich tans. The nape of the head is black, with three or four crossbars of deep buff or rufous. The feet and toes, which are small and weak, are brownish gray to reddish brown.
Woodcock have large eyes located high in the head, and their visual field is probably the largest of any bird, 360° in the horizontal plane and 180° in the vertical plane.
The Woodcock uses its long bill to probe in the soil for food, mainly invertebrates and especially earthworms. A unique bone-and-muscle arrangement lets the bird open and close the tip of its upper bill, or mandible, while it is sunk in the ground. Both the underside of the upper mandible and the long tongue are rough-surfaced for grasping slippery prey.
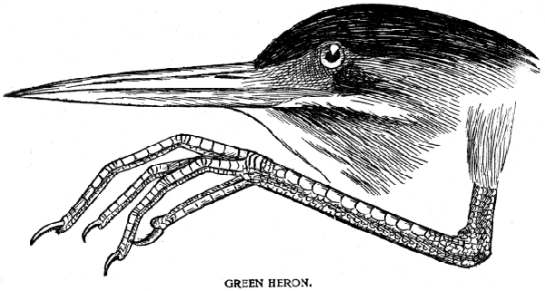
Color Key – Many of the members of the family Scolopacidæ are probing Snipe. The Woodcock, Wilson Snipe, and Dowitcher are good examples. Their bill is long and sensitive and they can curve or move its tip without opening it at the base. When the bill is thrust into the mud the tip may therefore grasp a worm and it thus becomes a finger as well as a probe.
Besides the American Woodcock, there are these: (Photos from IBC)
Eurasian Woodcock (Scolopax rusticola)
Amami Woodcock (Scolopax mira)
Javan Woodcock (Scolopax saturata) or Dusky
New Guinea Woodcock (Scolopax rosenbergii)
Bukidnon Woodcock (Scolopax bukidnonensis)
Sulawesi Woodcock (Scolopax celebensis)
Moluccan Woodcock (Scolopax rochussenii)
American Woodcock (Scolopax minor)
Birds Illustrated by Color Photography – Revisited – Introduction
The above article is the first article in the monthly serial that was started in January 1897 “designed to promote Knowledge of Bird-Live.” These include Color Photography, as they call them, today they are drawings. There are at least three Volumes that have been digitized by Project Gutenberg.
To see the whole series of – Birds Illustrated by Color Photography – Revisited
*
(Information from Wikipedia and other internet sources)
Next Article – The American Scoter
The Previous Article – The Anhinga Or Snake Bird
Links:
Scolopacidae – Sandpipers, Snipes
American Woodcock – All About Birds
American Woodcock – Wikipedia
*