“Flag That Bird!” (Part 1)
We will rejoice in thy salvation, and in the name of our God we will set up our banners; may the Lord fulfil all thy petitions. (Psalms 20:5 — numbered as 20:6 in Hebrew Bible)

Orni-Theology
“Flags” and “banners” herald symbolic messages and institutions, such as a nationality, a dynasty, a military force, or some other kind of organization. In holy Scripture, the term “flag” (in the KJV) refers to riparian or lacustrine wetland plants, which somewhat resemble banners in their physical appearance (see Job 8:11; Exodus 2:3,5; Isaiah 19:6). The term “banner” denotes the word “flag” as it is commonly used today (see Exodus 17:15; Song of Solomon 2:4 & 6:4,10; Psalms 20:5 & 60:4; Isaiah 13:2).

Whenever birds are featured on a national flag (or on its “armorial banner” version, or on a national province or department), the odds heavily favor the banner-bird being an eagle. Flags affiliated with American showcase the bald eagle; other nations usually present a golden eagle, like Mexico, or sometimes a mythical “double-headed” eagle, like Mount Athos.

flag of Mexico ©WikiC
Consider – for just a few representative examples – the eagles that appear on the flags – some present, some past — of these national and state/provincial flags: Albania; American Samoa; Austria (armorial flag); Brandenburg, Germany; Ecuador (armorial banner); Egypt; Geneva, Switzerland; Germany (armorial flag ); Iowa; Italian president’s flag (AD1880-AD1946); Jordan (armorial banner); Mexico; North Dakota; Oregon (front side of state flag); Pennsylvania; Poland (armorial flag); Prussia (armorial banner, AD1819-AD1850); (Moldova; Mount Athos (autonomous Greek protectorate); Russian Czar’s banner (18th century A.D.); Serbia (during AD1882-AD1918); Silesia (until absorption by Prussia in AD1742 – parts of Silesia now lay within Poland, Germany, and the Czech Republic); United States Coast Guard and Marine Corps; Utah; Virgin Islands (of the USA); Zambia; etc.
So what about the other birds? Do any other birds get to show off their plumage on a national flag? Yes, but just a select few. Although this listing is likely incomplete (and it will be presented as a mini-series, God willing), herebelow are some non-eagle birds that appear on the official flags of some countries of the world.
For starters, consider the common – yet ubiquitously valuable – Chicken.
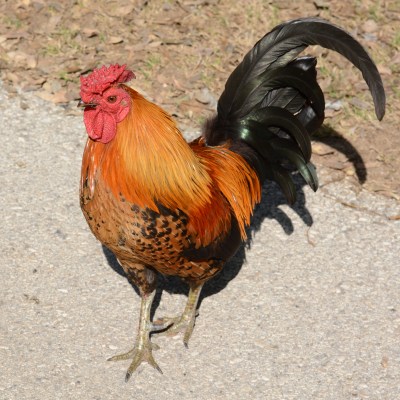

Gallic Chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) ©WikiC
Gallic Chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus).
The Gallic Chicken appears on the flag of Wallonia, Belgium.
Wallonia is a region of Belgium, where French is the language usually spoken. (In Flanders, however, Flemish is spoken; Brussels is bilingual.) The “Walloon Cock” (i.e., rooster of Wallonia) marches prominently at the center of the regional flag of Wallonia, Belgium.
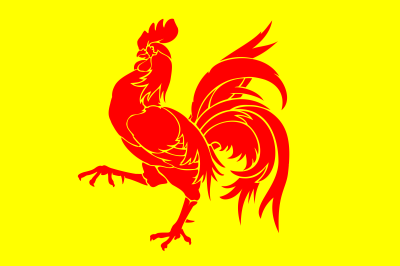
Flag of Wallonia
During New testament times the country of France (and additional lands that border it) was called “Gaul”, and the symbol of Gaul was the “Gallic cock” (Gallus gallus domestic), i.e., a strutting rooster – the adult male of the domestic Chicken, deemed a subspecies of the Red Jungle-fowl (Gallus gallus). “The cock is a traditional Gallic [i.e., Gaelic/Celtic] emblem and [it] recalls Wallonia’s linguistic and cultural ties with France.” [Quoting Alfred Znamierowski, The World Encyclopedia of Flags (London: Hermes House, 2002), page 146.] Chickens are bred and eaten all over the world – they even roam the streets of Key West, Florida! Can you imagine life without chicken? – think of the almost endless variety of culinary uses of chicken meat and chicken eggs! Vive le poulet!
The next bird on this list is “bird hawk”, i.e., an accipiter hawk.
Among the birds of prey (“raptors”), there are two main categories of “hawks”: (1) eagle-or-buzzard-like “buteos” (famous for snatching rodents, lizards, fish, and snakes); (2) and smaller forest-frequenting “accipiters” (famous for snatching birds). Some would “lump” falcons with accipiters; other do not. Other groups within the greater “hawk family” include eagles, kites, harriers, vultures, and various “buzzards”.
Buteos include such birds as Red-tailed Hawk, Swainson’s Hawk (which also eats insects), Ferruginous Hawk, Eurasian Buzzard, Broad-winged Hawk, and Osprey.
Accipiters are the smaller category of hawk-like birds — the “true hawks” — which include the likes of Cooper’s Hawk, Northern Goshawk, Eurasian Sparrowhawk, Sharp-shinned Hawk, etc. “Accipiters are woodland, bird-catching hawks. They rely on surprise and a blurring burst of speed to overtake prey. Short, broad wings provide great acceleration, and slim bodies create little drag.” [Quoting Jack L. Griggs, All the Birds of North America (HarperCollins, 1997), page 66 .] The smaller size of accipiters is a more fitting design for darting in between and around tree branches and shrubbery. “An accipiter, like the Cooper’s hawk, can chase a songbird through a maze of trees without seeming to slow down, using its long tail as a rudder to help maneuver. If a songbird does escape the initial attack, it is likely to survive the encounter, for accipiters are sprinters … [who] seldom engage in prolonged tail chases.” [Again quoting Griggs, All the Birds of North America, page 66.]

Northern Goshawk (Accipiter gentilis) ©USFWS
Northern Goshawk (Accipiter gentilis).
The Northern Goshawk appears on the flag of the Azores, an Atlantic Ocean-surrounded archipelago. These volcanic islands, located southwest of the European continent, arose from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, constitute an autonomous protectorate of Portugal.

Portuguese Flag (PD)
The word “Azores’ derives from açor, the Portuguese word for “goshawk” (which means “goose-hawk”). Yet it is ironic that both the name and flag of the Azores feature the Northern Goshawk (an accipiter common in continental Europe), because many historians doubt that the Northern Goshawk was a common resident of there, when the Azores were discovered by Portuguese sailors during the AD1400s. Many think that a local variety of the Eurasian Common Eurasian (Buteo buteo) was mistaken for the Northern Goshawk (Accipiter gentilis) – yet nonetheless the name “Azores” (meaning “goshawks”) stuck. Accordingly, the depiction of a goshawk, matching the archipelago’s name, was superimposed onto the Azores’ territorial flag.)
The next flag-featured bird is a spectacularly colored fowl, famous for its fan-like display of extravagant covert plumage, the Peafowl. Many call this iridescence-decorated fowl the “peacock”, although it is only the male that is appropriately called “peacock”; the female is a “peahen” and the young are “peachicks”. There are three types of peafowl: (1) the Blue Peafowl (a/k/a “Indian Peafowl”) of India and Ceylon; (2) the Green Peafowl of southeastern Asia (native to Burma, Indochina, and the Indonesian island of Java); and (3) the Congo Peafowl (native to the Congo River’s drainage basin in Africa).

(Javan) Green Peafowl (Pavo muticus muticus) by Lee at Zoo Miami
Green Peafowl (Pavo muticus).
The Green Peafowl appeared, briefly (AD1939-AD1941), on the British territorial flag of “British Burma” – then a British Commonwealth colony. (Burma is now called “Myanmar”.) That colonial flag contained a Green Peafowl prominently displaying its famous covert feathers.

Flag of the Third Burmese Empire (PD)
The Green Peafowl, historically, had symbolized pre-colonial regimes of Burma.
For example, the flag of the “Third Burmese Empire” (Konbaung Dynasty, AD1752-AD1885 – a/k/a “Alompra Dynasty”, which ultimately lost the Anglo-Burmese Wars – after persecuting the Great Commission efforts of Baptist missionary Adoniram Judson, who translated the Holy Bible into Burmese), consisted of a fan-tailed Green Peafowl, superimposed on a white background.

Peafowl on Flag of the Third Burmese Empire (PD)
One more non-eagle bird, displayed on a national flag, will be included, below. (The remainder must arrive on this blogsite another day, God willing.) The next bird we will “flag” is a parrot.

Sisserou Parrot (Amazona imperialis), a/k/a Imperial Amazon Parrot.
The Sisserou Parrot is a montane rainforest-dwelling parrot “endemic” to the Caribbean island nation of Dominica (not to be confused with another Caribbean country, Dominican Republic). The term “endemic” means limited to that one location, so the Sisserou Parrot is native only to the island nation of Dominica. And what a beautiful parrot it is! As the national bird of Dominica, it is showcased “center-stage” on Dominica’s flag.

Dominica’s-Flag ©WikiC

Sisserou Parrot Insert (Amazonaon Dominic) Flag ©Flickr-
The flag’s depiction of the parrot is dominated by green and purple, with the beak and talons presented as yellow. This coloring approximates the real parrot, though the “real thing” is obviously more beautiful! The Sisserou is known to keep company with other parrots of Dominica, including the also-endemic Dominican Blue-faced Amazon Parrot (Amazona arausiaca, a/k/a “Red-necked Amazon” – no jokes about “rednecks”, please!)
There are more official birds to “flag”: British Antarctic Territory (penguin); Saint Helena, British crown colony in the southeastern Atlantic Ocean (Saint Helena Plover, a/k/a “wirebird”); Fiji (dove); Kiribati (frigatebird); Papua New Guinea (bird of paradise); Australian state of Western Australia (black swan); Australian state of South Australia (piping shrike, n/k/a white-backed Australian magpie); royal standard flag of Tonga (dove); Bolivia (condor); and Uganda (crested crane).
Till this mini-series continues, “flag those Jehovah-nissi birds!” Yet more importantly, keep in mind that the Creator of all birds, flagged or otherwise, is JEHOVAH-NISSI (“the LORD our banner”), the One to Whom we pledge our ultimate allegiance!
And Moses built an altar and called the name of it Jehovah-nissi. (Exodus 17:15)
*
More Articles by James J. S. Johnson
*






































